Git Version Control
Version control system
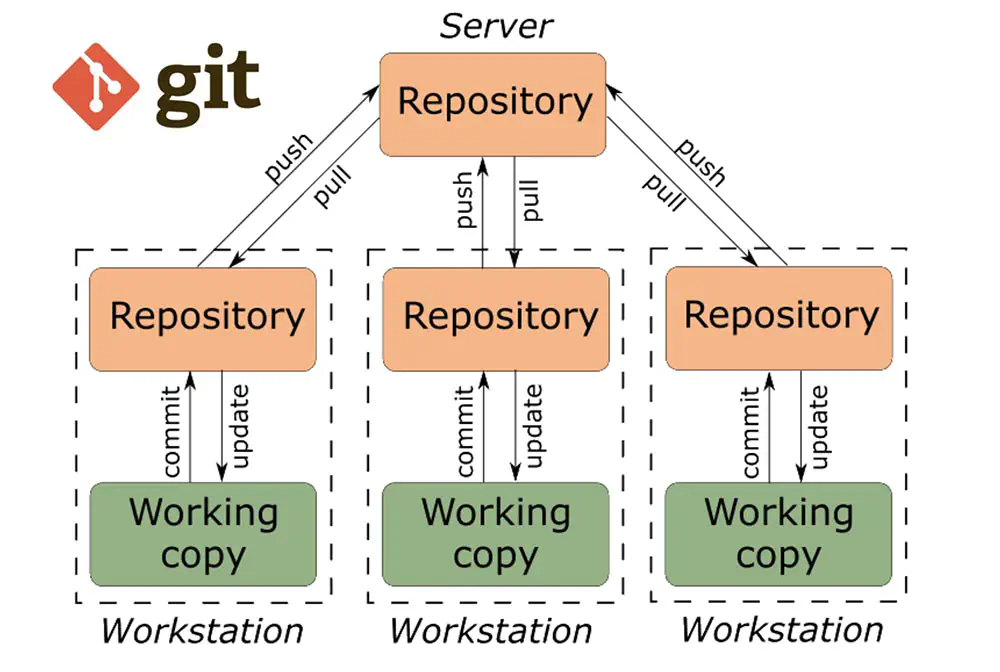 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: Unsplash
Overview
Version control systems (Version Control System, VCS) are used when working with several people under a project.The usual main tree of the project is stored in a local or remote repository to which access is configured for project participants.When making changes to the content of the project, the version control system allows you to fix them, combine changes made by different project participants, roll back to any earlier version of the project, if required. In classical version control systems, a centralized model is used, assuming a single repository for storing files. Most version control functions are performed by a special server. The project participant (user) receives the version of files he needs before starting work through certain commands.After making changes, the user places the new version in the repository. At the same time, previous versions are not deleted from the central repository and you can return to them at any time.The server can save the full version of the changed files, and produce the so-called data- compression—save only changes between successive versions, which reduces the amount of data stored. Version control systems support the ability to track and resolve conflicts that may arise when several people work on a single file.You can merge (merge) the changes made by different participants ( automatically or manually), manually select the desired version, cancel the changes altogether or lock the files for modification. Depending on the settings, the lock does not allow other users to get a working copy or prevents the change a working copy of the file by means of the OS file system, thus providing privileged access to only one user working with the file. Version control systems can also provide additional, more flexible functionality.For example, they can support working with multiple versions of a single file, keeping a general history of changes up to the point of branching versions and their own change histories of each branch.Moreover, information is usually available about which of the participants, when and what changes were made.The usual this kind of information is stored in the change log, access to which can be restricted. Unlike the classical ones, in distributed version control systems, a central repository is not mandatory. Among the classic Venture capitalists, the most famous are CV, Subversion, and among the distributed ones - Git, Bazaar, Mercurial. The principles of their work are similar, they differ mainly in the syntax of the commands used in the work.